The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) and Mastercard are partnering to explore the possibility of making their digital health pass solutions interoperable. Mastercard explained that the interoperability isn’t just between different health credentials but also between other technologies such as passports or identity and tickets.
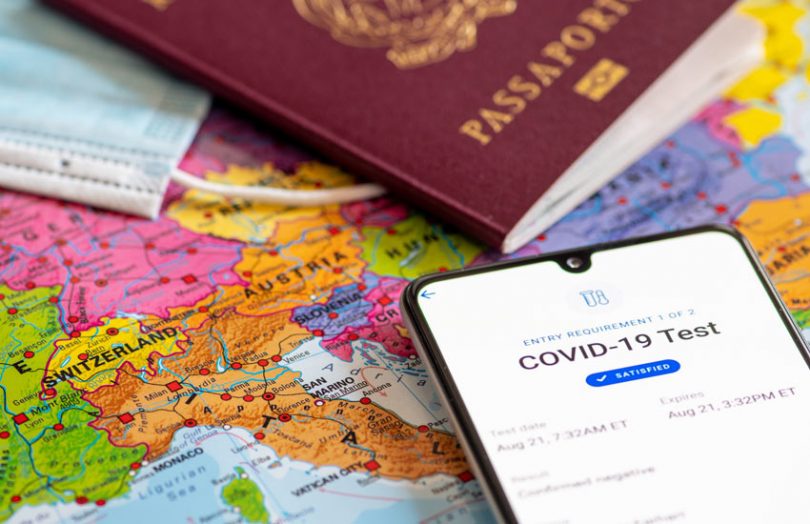
As border restrictions ease up and travel begins to return to normalcy, most governments are requiring incoming travelers to present negative Covid-19 test results, and there are discussions about the feasibility of imposing proof of vaccination as well. The proofs are commonly accepted at border control in paper form. Beyond travel, immunity passports are relevant for admission to events and access to offices.
The problem with paper certificates is that they are easy to falsify, take time and resources to be validated, and can be spoiled or lost. As such, exploring digital solutions that foster a trustworthy, traceable, and convenient health credentialing process will be essential for a smooth transition to traveling.
Article continues …
Want the full story? Pro subscribers get complete articles, exclusive industry analysis, and early access to legislative updates that keep you ahead of the competition. Join the professionals who are choosing deeper insights over surface level news.






