The European Central Bank (ECB) published a working paper exploring the popularity of Bitcoin in emerging economies. It found speculation impacts cryptocurrency prices worldwide. However, in emerging economies, the instability of the local fiat currency is an additional driver of demand. Despite the price volatility, Bitcoin may be viewed as a store of value by those holding unstable local currencies.
Fluctuating advanced economy currencies did not impact cryptocurrency activity. For example, during the period the Australian Dollar, British Pound and Japanese Yen were relatively unstable, but didn’t impact crypto demand.
The research also found that Bitcoin is used for payment transactions in some emerging economies. That’s particularly true for cross border payments where economies have capital controls or for receiving remittances at a lower cost. Our own cursory analysis below indicates remittances could be a major factor.
Additionally, the research found a correlation in payment usage in countries that have underdeveloped traditional finance systems. Plus countries with younger, less risk averse populations also use Bitcoin more.
Rather than basing conclusions on anecdotal evidence, it looked at transactions against Bitcoin in local currencies. It used off-chain data from popular P2P exchanges rather than cryptocurrency exchanges which are more likely to have wash trades.
The IMF previously expressed concerns regarding the potential of cryptocurrency to impact economies with volatile countries and as a means to circumvent controls. In 2019, 90% of IMF member countries had capital controls.
“Our findings clearly point to potential financial stability risks in EMDEs with low levels of financial development and unstable fiat currencies,” the ECB report concludes. It notes that the price volatility of Bitcoin could discourage some, but stablecoins based on reserve currencies might become more widely used.
A crossover with remittances?
Given two of the key drivers are unstable currencies and the need for cross border remittances, in our view, it is worthwhile determining which is a bigger influence. That’s because the G20 is trying to address remittance costs, whereas volatile currencies are a far trickier issue.
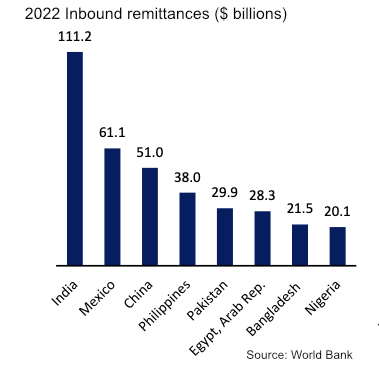
A quick (admittedly cursory) analysis indicates that remittances could be a major factor. Four of the top eight economies with the most inbound remittances are in the top ten for crypto. Regarding local fiat currency instability, only one of the top ten most volatile jurisdictions appears on the list. However, if you look further down the list, several others are big crypto users.
Chainalysis ranked countries in terms of cryptocurrency adoption. The top ten are:
- India
- Nigeria
- Vietnam
- USA
- Ukraine
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Pakistan
- Brazil
- Thailand
According to World Bank research, these are the top eight countries for inbound remittances:
Below is data on fiat currency volatility from the ECB report: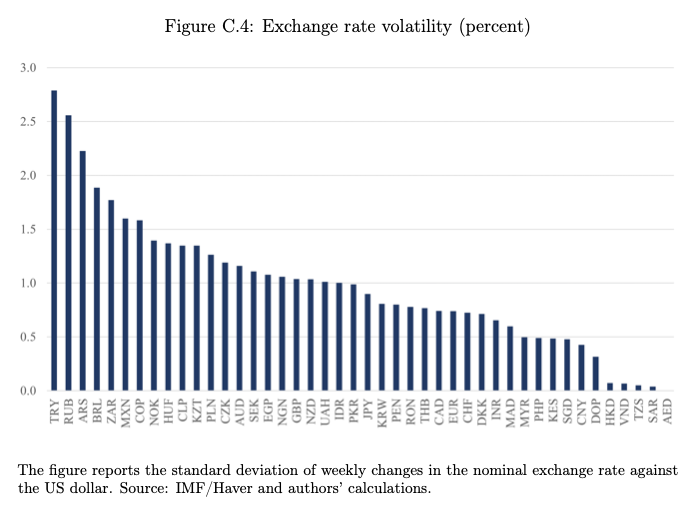
The ECB research’s findings were particularly during and post COVID, when migrant workers may have been stuck offshore.
Mexico has both a volatile currency and considerable inbound remittances. Yet it only ranks in 16th spot on the Chainalysis list. There are two potential explanations. Firstly, crypto is banned, similar to 11th-ranked China. Secondly, while Mexico is not considered dollarized, the U.S. dollar is widely used, so there is an alternative store of value and medium of exchange.






